This article outlined by MiniTool gives a complete review of Ethernet. It elaborates on its definition, function, work policy, types, and examples. Besides, this post also compares Ethernet with splitter, hub, and router.
What Is an Ethernet Switch?
An Ethernet switch, also called an Ethernet box, creates networks and makes use of multiple ports to communicate between devices within the Local Area Network (LAN). Ethernet switches are different from routers, which connect networks and use only a single LAN and Wide Area Network (WAN) port.
Ethernet switching connects wired devices like computers (desktops and laptops), servers, routers, and printers to a LAN. Multiple Ethernet switch ports enable faster connectivity and smoother access across multiple devices.
How Does an Ethernet Switch Work?
The following are the terms and their functions of Ethernet switches.
#1 Frames
Ethernet frames are sequences of info traveling over an Ethernet network to move data between computers. They include source addresses where the traveling data come from and destination addresses where the data is traveling to.
#2 Frame Flooding
Entries in an Ethernet switch’s forwarding database may drop from the list if the switch does not witness any frames from a certain source over some time. If any entry is dropped but traffic resumes from the entry at a later time, the switch will forward the frame to all switch ports to search for its correct destination. When it connects to that destination, the switch will learn the correct port again. Then, frame flooding stops.
#3 Address Learning
Ethernet switches control how frames are transferred between switch ports, making decisions on how traffic is forwarded based on 48-bit media access control addresses adopted in LAN standards. They can learn which devices are on which segments of the network using the source addresses of the frames it receives.
#4 Transparent Bridging
With transparent bridging, an Ethernet switch automatically starts working without requiring any configuration on a switch or changes to the computers in the network.
#5 Traffic Filtering
Once an Ethernet switch has built a database of addresses, it can smoothly choose how it filters and forwards traffic. As it learns addresses, the switch checks frames and makes decisions based on the destination address in the frame. It is also able to isolate traffic to only those segments needed to receive frames from senders.
#6 Multicast Traffic
LANs can not only transmit frames to single addresses but also send frames to multicast addresses that are received by groups of endpoint destinations. Among those multicast addresses, broadcast addresses are a special form. They group all endpoint destinations in the LAN.
Ethernet Switch Types
Generally, there are two kinds of Ethernet switches, managed Ethernet switch and unmanaged Ethernet switch.
Managed Ethernet Switch
Managed Ethernet switches are the switches that can be managed and programmed to deliver certain outcomes and conduct certain tasks. They achieve those operations by adjusting speeds and combining users into subgroups to monitor network traffic.
Unmanaged Ethernet Switch
Unmanaged Ethernet switches, on the other hand, refer to switches that have no user configuration. They can be plugged in and turned on.
Best Ethernet Switches
Below content lists some popular Ethernet Switches in the market like Amazon, Best Buy, Walmart, etc.
- Cisco Business CB110-8T-D Unmanaged switch
- NETGEAR Nighthawk S8000 8-port Gigabit managed gaming switch
- Tenda SG108 (8-port Gigabit Ethernet network switch)
- Netgear 8 port Gigabit unmanaged Ethernet Switch (GS108)
- Netis ST3124P 24 port 10
- D-Link Ethernet switch (DGS-1008G)
- TP-Link TL-SG108
- OOSSXX 8 port Gigabit Poe (Power over Ethernet) switch
Ethernet Splitter vs Switch
An Ethernet splitter is used to transform one Ethernet connection into several. It is a small “transit” with 3 Ethernet ports, 2 on one side and 1 on the other.
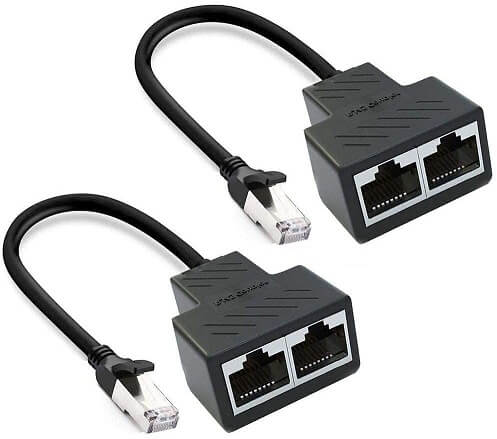

The Ethernet splitter does not increase the number of devices connected via Ethernet. Once you “merge” to cables from the router into one cable using one splitter, you need a splitter at the other end to “unsplit” the connection back into two cables that will connect two devices. So, 2 Ethernet splitters are necessary each time.
The major disadvantage of the Ethernet splitter is that it reduces the number of utilized wires in a Cat 5e Ethernet cable and reduces the data throughput from 1000Mbps to 100Mbps. So, compared with an Ethernet switch or hub, an Ethernet splitter is not recommended.
Ethernet Switch vs Hub
An Ethernet hub or simply hub is a network hardware device for connecting multiple Ethernet devices together and making them act as a single network segment. It is also known as a network hub, repeater hub, multiport repeater, as well as active hub.
Ethernet hubs are similar to Ethernet switches in that connected devices on the LAN will be wired to them through multiple ports. The biggest difference between them is that Ethernet hubs share bandwidth equally among ports while Ethernet switches can devote more bandwidth to certain ports without degrading network performance.
Therefore, when many devices are active on a network, Ethernet switches offer more robust performance than Ethernet hubs. And, Ethernet hubs have been replaced by Ethernet switches in a wide range except in very old installations or specialized apps. In 2011, connecting network segments by hubs or repeaters is deprecated by IEEE 802.3.
Ethernet Switch vs Router
Compared with Ethernet switch, Ethernet router connects networks to other networks, usually connecting LANs to WANs. Routers are usually placed at the gateway between networks and route data packets along the network.

Most corporate networks take advantage of the combinations of switches, hubs, and routers; as well as wired and wireless technology.
Related article: Router VS Switch: What Is the Difference Between Them?
![[Solved] 9 Ways: Xfinity WiFi Connected but No Internet Access](https://images.minitool.com/minitool.com/images/uploads/2021/02/xfinity-wifi-connected-but-no-internet-access-thumbnail.png)