The Task Manager is an operating system component available in Windows. It enables users to view each task currently running on the computer, each process, and the overall performance of the computer... Get more information from this article!
Definition of Task Manager
Task Manager (formerly known as Windows Task Manager) is a task manager, system monitor, and startup manager included with all versions of Microsoft Windows since Windows NT 4.0 and Windows 2000.
Windows Task Manager provides information about computer performance and shows detailed information about the programs and processes running on the computer, including name of running processes, CPU load, commit charge, I/O details, logged-in users, and Windows services; if connected to the network, you can also view the network status and quickly understand how the network works.
Microsoft improves the task manager between each version of Windows, sometimes quite dramatically. Specifically, the task managers in Windows 10 and Windows 8 are very different from those in Windows 7and Windows Vista, and the task managers in Windows 7 and Vista are very different from those in Windows XP. A similar program called Tasks exists in Windows 98 and Windows 95.
How to Open the Task Manager
Starting Task Manager is always a concern for many of you. Now we will list some easy and quick ways for you to open it. Some of them might come in handy if you don’t know how to open a Task Manager or you can’t open Task Manager the way you’re used to.
You are probably familiar with the way that pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete on your keyboard. Before Windows Vista was released, this way can bring you directly to Task Manager.
Starting with Windows Vista, pressing Ctrl+Alt+Delete now brings you to the Windows Security interface, which provides options for locking your PC, switching users, signing out, changing a password, and running Task Manager.
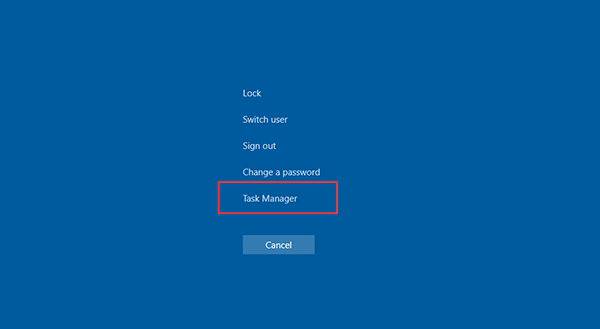
The quickest way to start Task Manager – assuming your keyboard works normally – is to press Ctrl + Shift + Esc.

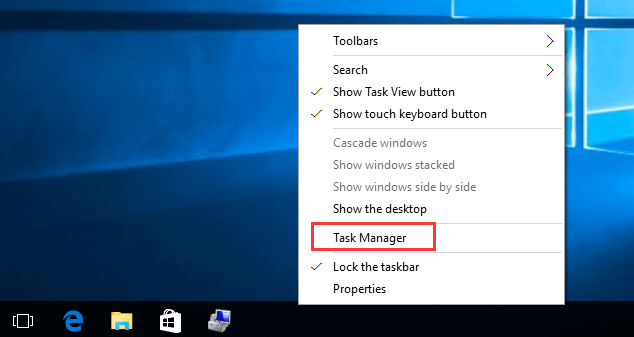
If you prefer using a mouse over a keyboard, one of the quickest ways to launch Task Manager is to right-click on any blank area on the taskbar and select Task Manager. Just need two clicks.
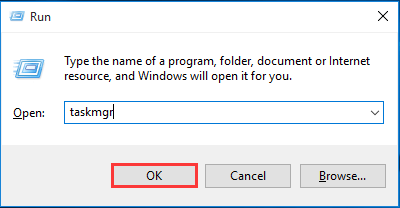
You can also run Task Management by hitting Windows+R to open the Run box, typing taskmgr and then hitting Enter or clicking OK.
In fact, you can also open the Task Manager by Star menu, Windows Explorer, or creating a shortcut… While we have listed these four convenient ways which are totally enough for you.
Explanation of the Tabs in Task Manager
Now we are going to discuss all the useful tabs you can find in the Task Manager nowadays, mostly in Windows 8 and Windows 10.
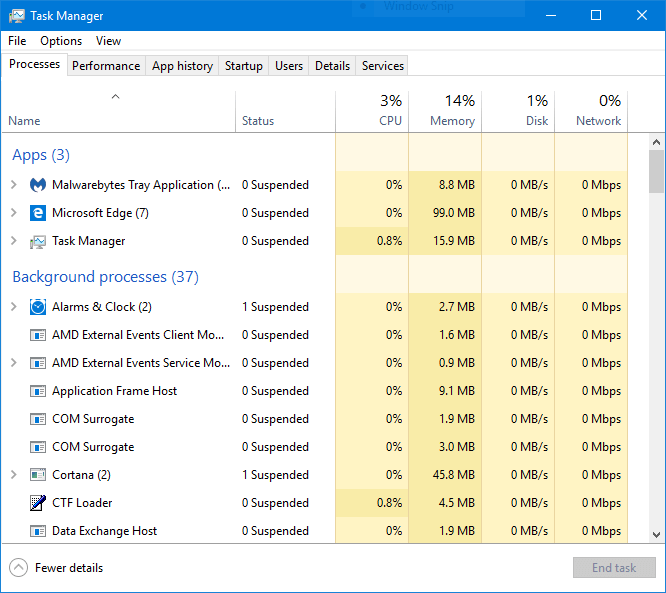
Processes
The Processes tab contains a list of all running programs and applications on your computer (listed under Apps), as well as any background processes and Windows processes that are running.
In this tab, you can close running programs, see how each program uses your computer resources, and more.
The Processes tab is available in all versions of Windows. Starting with Windows 8, Microsoft has combined the Applications and Processes tab into the Processes tab, so Windows 8/10 displays all running programs in addition to processes and services.
Performance
The Performance tab is available in all versions of Windows that is a summary of what’s going on, overall, with your major hardware components, including CPU, memory, disk drive, Wi-Fi, and network usage. It displays how much the computer’s available system resources are being used, so you can check the valuable information.
For example, this tab makes it easy to see your CPU model and maximum speed, RAM slots in use, disk transfer rate, your IP address…Newer versions of Windows also display usage charts. What’s more? There is a quick link to the Resource Monitor at the bottom of this tab.
App History
The App History tab displays the CPU usage and network utilization that each Windows app has used from the date listed on the screen until the time you enter Task Manager. App History is only available in Task Manager in Windows 10 and Windows 8.
Startup
The Startup tab shows every program that is launched automatically each time you start your computer, along with several important details about each program, including the Publisher, Status, and Startup impact which is the most valuable information – shows the impact rating of high, medium or low.
This tab is great for identifying and then disabling programs that you don’t need them to run automatically. Disabling Windows auto-start programs is a very simple way to speed up your computer. Startup tab is only available in Task Manager in Windows 10 and Windows 8.
Users
The Users tab shows users currently signed in to the computer and the processes are running within each. The Users tab is available in all Windows versions of Task Manager but only shows processes that each user is running in Windows 10 and Windows 8.
Details
The Details tab contains full details of each process running on your computer. The information provided in this tab is useful during advanced troubleshooting. Details tab is available in Task Manager in Windows 10 and Windows 8, and the features of the Processes tab are similar to Details in earlier versions of Windows.
Services
The Services tab is available in Task Manager in Windows 10, 8, 7, and Vista that shows all of the Windows Services currently running on the computer with the Description and Status. The status is Running or Stopped, and you can change it.
What to Do in the Task Manager?
Task manager always gives you some limited control over those running tasks, like set process priorities, processor affinity, start and stop services, and forcibly terminate processes.
Well, one of the most common things done in Task Manager is to use End Task to prevent programs from running. If a program no longer responds, you can select End Task from the Task Manager to close the program without restarting the computer.