This post is going to introduce you a protocol – DHCP, including its general and dedicated meaning.
What Is DHCP
DHCP is one of the protocols in Internet Protocol Suite, which is a network management protocol utilized on Internet Protocol networks. What does DHCP stand for? DHCP stands for Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol.
DHCP is a protocol used for assigning dynamic IP addresses to devices on a network. By using dynamic addressing, a device can have a different IP address every time it connects to the network. They can use network services like DNS, NTP, as well as any communication protocol based on UDP or TCP.
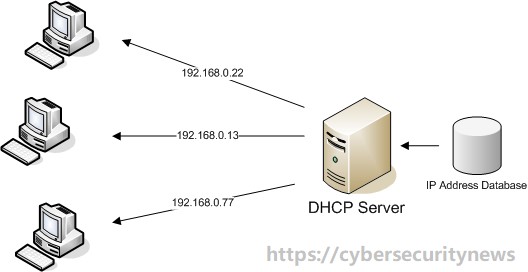
Moreover, DHCP assigns the subnet mask, default gateway address, domain name server (DNS) address, and other pertinent configuration parameters. DHCP is an upgraded version of an older protocol called BOOTP. Actually, the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is an indispensable part of the DDI solution (DNS-DHCP-IPAM).
On some systems, the IP address of the device changes even when it is still connected. DHCP supports a combination of static and dynamic IP addresses as well. With DHCP, errors occurring in the process of manually assigning IP addresses decrease sharply. In addition to that, DHCP can stretch IP addresses by limiting how long a device can maintain an individual IP address.
What’s DHCP meaning? You may have learn the fact from the above content.
Recommended: An Overview of HDCP (High-Bandwidth Digital Content Protection)
Main Components of DHCP
It is vital to learn the main components of DHCP. They are summarized as follows.
DHCP server: It is a network device that runs the DHCP service, containing IP addresses and related configuration information. It is most likely a server or a router, but it also could be anything acting as a host like SD-WAN appliance.
DHCP client: It is the endpoint that receives configuration information from a DHCP server. It can be a computer, mobile device, IoT endpoint or anything demanding connectivity to the network. Most of them are set to receive DHCP information by default.
DHCP relay: A router or host listens for client messages being transferring on the network and then send them to a configured server. Then the server sends back to the relay agent that passes them along to the client. It can be utilized to centralize DHCP servers rather than having a server on every subnet.
IP address pool: The IP addresses in this range are available for DHCP clients. These addresses usually are sent from the lowest to highest.
Subnet: It refers to IP networks that can be partitioned into segments, which helps keep networks manageable.
Lease: It is the length of time that a DHCP client can hold the IP address information. Once the lease expires, the client has to renew it.
The above elements are the main components of DHCP. What can you benefit from Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol? Move to the next section to get the detailed information.
What Is Secure Copy Protocol (SCP) & How Does It Work
Benefits of DHCP
The following are the main benefits that you can gain from DHCP.
- Simplified IP address management: Most users are not technically proficient enough to find the IP address information on computers and assign it. Under the help of DHCP, you don’t have to worry about it.
- Accurate IP configuration: The IP address configuration parameters should be accurate. Otherwise, it is very likely to make mistakes. Errors like typographical errors are hard to solve. Fortunately, the use of DHCP minimizes that risk because of its accurate IP configuration.
- Decreased IP address conflicts: All the connected devices must have an IP address. More importantly, the IP address can only be used once and can’t be same on two hosts. If it is configured manually, errors probably occur. With DHCP, your device will be assigned a different IP address each time you connect to the network.
- Automation of IP address administration: In traditional way, network administrators need to assign and cancel addresses manually. It is almost impossible to know the exact time that devices need to access and leave the network. The operations can be automated and centralized via DHCP.
- Efficient change management: It is easy to change addresses, scopes or endpoints by using DHCP. As the DHCP server is configured with the new information, the message will be sent to the new endpoints automatically. Hence, no network configuration is needed even if the network device is upgraded or replaced.
Recommended article: An Overview of Real-time Transport Protocol (RTP)
What’s is DHCP? This post has already made a reply. Read the post carefully to find the answer now!