This post will introduce you a computer terminology - localhost, including its definition, working theory, as well as common uses in daily life. If you are not clear about localhost, you can read this post to obtain the details.
Localhost Definition
What is localhost? In the world of computer networking, localhost is a hostname that stands for this computer. In most cases, localhost refers to your own computer, but it is not always identified with your PC.
Actually, local host has a separate IP address in most cases. The localhost that you often talk about refers to the server who uses your computer. To get more information about local host, please keep reading this post of MiniTool.
However, local host in fact is not simply a term but a domain name too. What does localhost mean? Like the words (Amazon.com, eBay.com, etc) you type in the address bar of your browser, localhost is also an IP address.
How does localhost work? Well, you will see the illustration in the next section.
To know more about networks, you can read this: Proxy vs VPN: The Main Differences Between Them
The Working Principle of Local Host
The IP addresses within a network are used to communicate with each other. Each participant in the network has its own unique address. Data packets that are sent by TCP/IP can reach the right place. The protocol pair Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP) are some leading features of Internet.
TCP/IP can also be used outside of the Internet in local networks. The allocation of public IP addresses and domain names are managed by an international organization called Internet Corporation for Assigned Name and Numbers (ICANN).
However, some address ranges (from 127.0.0.0 to 127.255.255.255) are kept for special purposes. The reason why that range is selected is not clear. It’s an all known fact that the IP addresses on the Internet are divided into different classes.
The first class (Class A) begins with 0.0.0.0 (reserved address) and ends with 127.255.255.255. So, you can see that 127 is the last block of Class A network. This crucial position may explain for its selection.
A Localnet can be established within the address range. These IP addresses are not uniquely assigned in the range. Besides, this range is also reserved by ICANN. After you enter an IP address or its corresponding domain name in the browser, the router will forward the request to the Internet and the correct server.
For instance, if you enter 172.217.0.0 in the browser, you will reach the homepage of Google. Differently, if you type 127.0.0.1, your requests will not be forwarded to the Internet. It is because that TCP/IP can recognize from the first block (127) that you don’t want to access the Internet.
On the contrary, you are calling yourself instead. What’s more, this will cause the loopback. Here comes the need of a loopback device. With this device, the back link to your computer works.
Top recommendation: What Is SSH (Secure Shell) & How Does It Work
3 Common Uses of Localhost
What is localhost used for? How to access localhost? You can find the answers in the content below. The localhost usually can be used for testing speed, checking program or Web application, and blocking site.
Test Speed
The main use of local host is web servers is for programming applications that need to communicate via the Internet. In the process of development, it is vital to check if the application works as expected. Before releasing any product, tests are required.
For this, developers often use a loopback to test them. One advantage for using localhost is that it can stimulate a connection and avoid a network detour. Another advantage is that localhost has a high speed. If you send a request to the Internet, it will take you over 100 milliseconds.
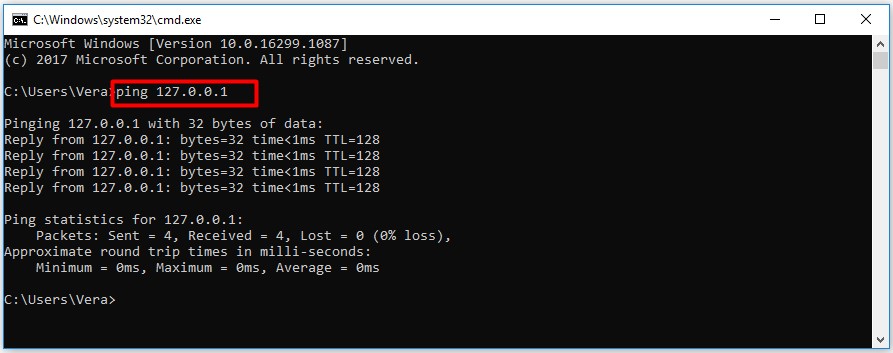
The things will different for localhost. If you send a ping to localhost, the longest time is just one millisecond. How to run a speed test over localhost? Here are steps.
Step 1: Open the Run window by holding Win + R keys, and then type cmd and click OK.
Step 2: In the pop-up window, enter ping 127.0.0.1 and hit the Enter key. After a while, you can receive the result.
Test Program or Web Application
Localhost also benefits developers who create web apps or programs that require an Internet connection. Your OS will become a simulated server when the loopback is caused. Hence, you are able to load vital files of the program or web application into the serer and check its functionality.
Block Site
If you want to block access to certain websites, localhost will help you do that. Actually, localhost is very useful for protecting you from entering harmful sites. All websites have an IP address. You can enter the homepage of a website because the DNS or Domain Name System that you type finds the proper IP address.
To make this process faster, computer will store a host file for each site that you visit. This file contains the IP address and the corresponding domain name of the website. Hence, if you change the IP address into 127.0.0.1 and voila, the site will redirect you to localhost.
You may also like this: File Server [Definition, Main Features, and Pro & Cons]