What is a backup? This article will illustrate you three backup types:Full Backup, Differential Backup, Incremental Backup.
Backup refers to copying data into an image file, which can be used to restore its contents to the original state if there is any data loss. MiniTool ShadowMaker supports creating image files for disks, partitions and system.
Normally, there are three backup types:
Full Backup
A Full Backup is an image file that contains a selection of files and folders, partitions or disk that can be completely restored to their original state. Full Backup is most space-consuming and time-consuming as each time the backup is carried out, all content will be imaged.
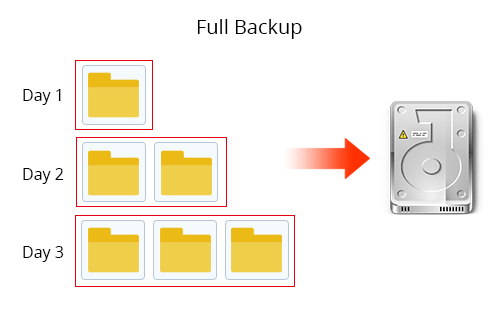
When it comes to restore, each copy of Full Backup image is independently from any other image file, and you can choose any copy to restore to the backup state.
Differential Backup
A Differential Backup is an image file that includes all changed or newly added data since the last Full Backup. As time progresses, each Differential Backup will contain more changes compared with the original Full Backup. Therefore, it requires progressively larger disk space.
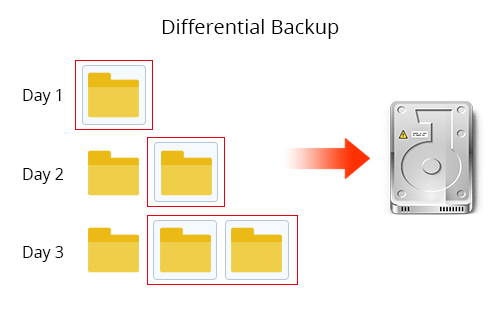
Differential Backup is closely related to a Full Backup. When it comes to restore, the last Full Backup and the latest Differential Backup are required for a full restoration.
Incremental Backup
An Incremental Backup is an image file containing only changed or newly added data since the last backup. Incremental Backups are created in a time sequence, and each backup copy should be kept safe for full restoration. The first incremental backup is a full backup, the second incremental backup only backs up the changed files since the full backup, and the third incremental backup only backs up the added data since the second incremental backup… So compared with Full Backup, an Incremental Backup takes smaller disk space and needs less time.
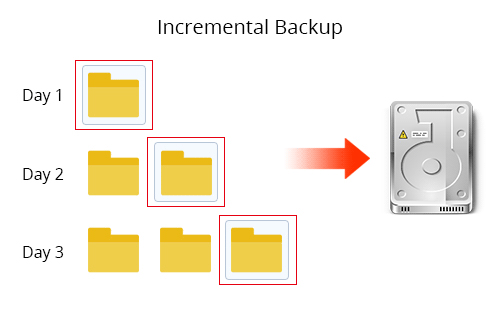
When it comes to restore, each copy of the backups is required to restore the most integrated data. However, you are able to pick a time in the past to restore.