Tape storage has long cemented itself as a natural backup tool by providing low-cost storage where performance wasn’t a priority. As the cost of HDDs has fallen, disk storage has become a worthy backup competitor. The following is about tape vs disk storage.
First, let’s see basic information about tape storage and disk storage.
What Is Tape Storage
A tape drive is a data storage device that reads and writes data on magnetic tape. Tape data storage is typically used for offline archival data storage. A tape drive must physically wrap the tape between the reels to read any particular data.
What Is Disk Storage
Disk storage is also referred to as drive storage. It is a general type of storage mechanism in which data is recorded by applying various electrical, magnetic, optical, or mechanical changes to the surface layers of one or more rotating magnetic disks.
Disk drives are devices that implement this storage mechanism. Notable types are hard disk drives (HDDs) containing non-removable disks, floppy disk drives (FDDs) and their removable floppy disks, and various optical disk drives (ODDs) and related optical media.
Tape vs Disk Storage
The main difference between the two forms of backup is the medium on which the data is backed up. Tape backup provides the ability to copy data packets from a hard drive to a tape cartridge for storage, backup, and recovery in the event of a computer crash or other failure.
In contrast, disk backup involves copying data and other information onto a hard drive for easy access later.
When start comparing tape backup to disk backup, there are five important factors to consider:
- Cost & Performance
- Security
- Ecosystem Benefits
- Reliability
- Pros and Cons
Tape vs Disk Storage: Cost and Performance
You need to consider the cost and performance of tape and disk storage. Both tape and disk backup technologies are cost-effective compared to higher-performance solid-state technologies. However, when comparing head-to-head on a per-TB basis, the tape is always the cheapest storage option. This is especially important when considering the large amount of data that modern organizations need to back up.
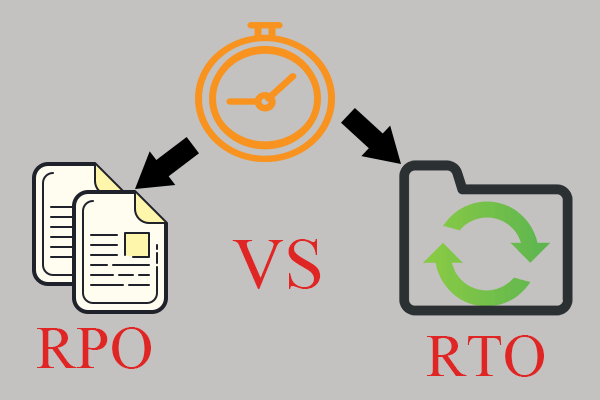
However, original cost alone isn’t the only important factor in determining your backup method. The recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO) quantify how much data can be lost and how quickly data can be recovered during an outage. These are key metrics that organizations use to calculate the monetary cost of data loss and application downtime.
Disk-based options provide faster backup and recovery than tape, and disks can help organizations meet their RTO and RPO goals. Consistently fast recovery may justify more expensive disk storage options in the long run.
Tape vs Disk Storage: Security
In addition to the low cost of tape and the superior performance of disk – are the inherent security features of offline tape storage. Tapes can be easily removed and stored offline, a feature often used for air-gapped protection against ransomware.
Some disk options can emulate this capability through logical Air-Gapping. Logical Air-Gapping also isolates storage by removing disk access from the host network. However, the physical removal of storage is different from traditional air gaps, so cyber attackers can find and exploit it.
Common methods of Air-Gapping include:
- Sharing files with the backup service account is the only account that has access.
- File storage on a completely different LAN segment.
- cloud-based storage account.
- Automatically timed connected file shares before the backup window.
Tape vs Disk Storage: Ecosystem Benefits
As tape storage has become less popular, there has been less innovation in this area. Disk storage vendors have been collaborating on industry standards to support software-defined storage; while they still exist, there is limited compatibility between tape storage vendors.
Even with the same vendor, some tape storage administrators have reported problems reading film written by another tape drive or head alignment differences between higher and lower capacity drives. Because this legacy technology is harder to use and more expensive to support, tape repair specialists are expensive, and recovery is harder than repairing damaged disks.
For example, disk storage backup vendor Altaro offers the following features that tape backup does not:
Filesystem-based backup storage (disk storage) on top of today’s modern file server infrastructure with all associated tools such as deduplication and encryption
- Various types of disk storage such as spinning disks, standard SSDs, NVME, etc.
- OS-level permissions and access control are provided with the storage system used.
- Access cloud-based storage.
- Easily managed with today’s technology management stack.
As you can see, disk storage offers many benefits, the main one being leveraging all the software-defined capabilities in the world today. For example, online deduplication is a very effective cost-saving tool, and while some tape drives may have this technology, they may not perform deduplication efficiently, depending on your software vendor.
Another thing of particular note is that you can use high-performance flash for backups if needed. For example, if you are in a highly regulated environment with high data change rates and strict RPO requirements, you may need flash memory to meet your data protection requirements. You won’t get that level of performance with tape storage.
Tape vs Disk Storage: Reliability
Since most tape systems lack modern storage management techniques, they may not be able to take advantage of deduplication, replication, data defragmentation, defragmentation, or other optimization and resiliency features. Even if a backup is made, there may be a lack of evidence that it is complete or that it is a data-consistent copy.
A small amount of data loss or corruption affects the entire tape drive and may not recover from the error. Tape storage typically has more resource contention and connectivity issues, making backups take longer to restore.
Not only does tape storage take up a lot of space, but it’s also fragile because the membrane of tape and the tape drives used to read and write data have many weaknesses. The film must not be exposed to magnetic fields, UV rays, sunlight, or radiation of any kind, otherwise, it will be damaged.
Tape storage must be used in a clean room, as any dust, heat, moisture, or creases can damage files, making it nearly impossible to use tape for fieldwork. Attempting to read defective film can further damage the tape and drive readers.
There are many moving parts, the drive head should be cleaned regularly, and all parts will wear out after a few years of use. Films must be stored vertically and handled with care to avoid damage that could result in damage. Since these tapes are separated from the physical storage system, they are also more prone to theft, and organizations are more likely to detect theft.
Tape vs Disk Storage: Pros and Cons
Tape Storage:
Pros:
- Tape provides mass storage – LTO (Linear Tape Open) is the leading tape backup format. With LTO-8, introduced in 2017, businesses can store up to 30TB of compressed data on a single tape. The LTO program roadmap shows that a future 12th generation LTO will store up to 480TB of compressed data on a single tape. This storage capacity should prove useful for the upcoming zettabyte apocalypse.
- Tape costs are very low – Tape is one of the least expensive options for long-term data archiving. Add an offsite tape library and it still outperforms a disk array of the same size. Cloud providers also often use tape as a low-cost storage tier.
- The tape lasts longer – According to a report by Bloomberg Businessweek, cassette tapes can last up to 30 years if kept clean and stored at the proper temperature. The disk can’t keep up.
Cons:
- You will spend more time finding data – With the LTFS (Linear Tape File System) feature, the seek time of backup tapes is greatly reduced. LTFS makes it easier to find data, similar to a disk. However, LTFS does not make tape seeks faster than disk.
- The tape needs maintenance – To avoid mistakes, this media must be stored in a pristine environment that protects its cartridges from dust and dirt. Tapes also need to be marked, recorded, and tested. This can be tedious and time-consuming.
- It’s been a long road to recovery – Storing tapes with offsite tape storage services does increase recovery time. That’s why you should choose to back up and store frequently used business-critical information on the premises or in the cloud.
Disk Storage:
Pros:
- It has a fast recovery – Finding a specific file on a disk is faster than finding a file on tape. If your disk is internal, you also don’t have to ship it offsite. (FYI: Cloud backups are also disk-based, just on someone else’s disk.)
- You will gain efficiency from deduplication – Deduplication allows you to deduplicate data to free up space. This means you can store data faster with less frequent full backups.
backup-and-recovery
Cons:
- It is not convenient – The disk system is always on and on the verge of running hot. That means you have to power and cool them.
- Always-on data comes with danger – Newer LTO tapes use WORM (write once, read many) security to prevent accidental overwriting. Once written, they are also physically removed from the network. Conversely, disk systems can be damaged by computer viruses. They can also be accidentally overwritten or reformatted.
- Get your head out of the cloud – If you think cloud storage might be the answer, you need to know that the cloud is another form of a disk that usually has higher data retrieval costs. The cloud has great uses, but still lacks the economics and longevity of large-scale, long-term archiving. Steep entry/exit charges are also a factor.
All in all, you can find that disk storage is more suitable for you. But you can still choose the tape storage.
How to Back up Data to Disk Storage
How to back up data to the disk storage? To do that, you can use the professional backup program – MiniTool ShadowMaker. It is designed to back up your files, folders, disks, partitions, and the operating system to safeguard your files and the computer.
Now, let’s see how to use MiniTool ShadowMaker to back up the files.
Step 1: Download MiniTool ShadowMaker from the following button, install and launch it.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 2: Click Keep Trial. After entering its main interface, go to the Backup page.
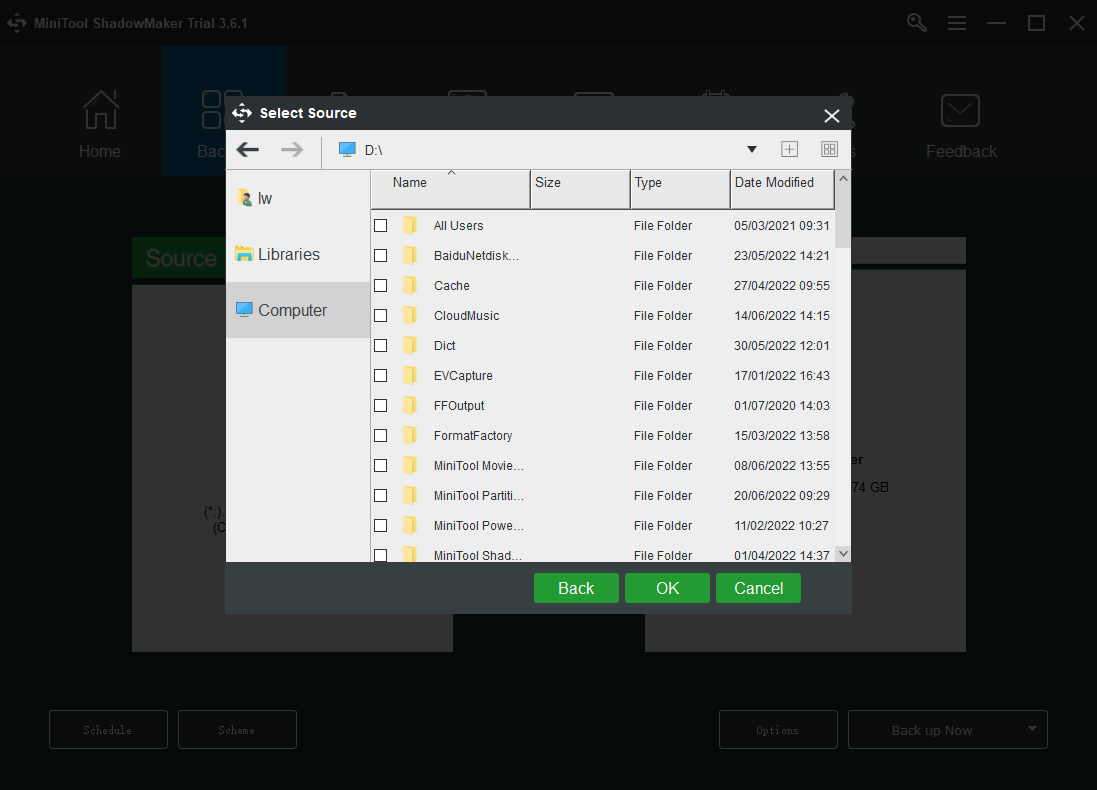
Step 3: Click the Source module and click the Folders and Files part. Choose the files you want to backup and then click OK to continue. You can choose a lot of files at the same time.
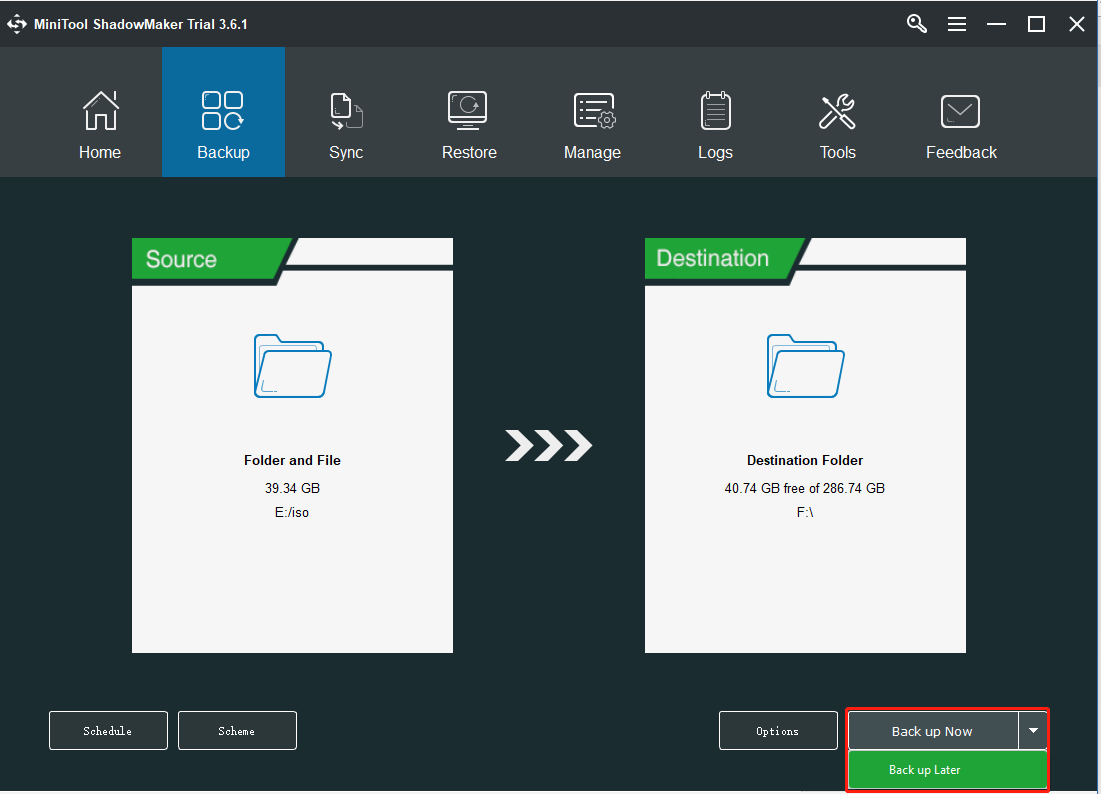
Step 4: Next, click the Destination module to choose a target path to save the backed-up files. You can choose to back up files to a local hard disk, an external hard drive, or a network drive. Then click OK to continue.
Step 5: After selecting the file backup source and destination, you can click Back up Now to start the process. You can also click Back up Later to delay the backup task.
Bottom Line
In this post, we show you some information on tape storage vs disk storage and you can know which one to choose. If you have any other ideas or questions when using MiniTool ShadowMaker, don’t hesitate to tell us by leaving a comment below or contacting our support team via the email [email protected]. We will reply to you as soon as possible.