Maybe you are confused about choosing NVMe or M.2 for your PC. Now, you can read this post from MiniTool to find the answer. This post provides a full and detailed introduction to NVMe vs M.2. Besides, you can know how to migrate the system to SSD.
SSD is a popular choice because of its speed. They read and write data much faster than your old hard drives, which can enhance your gaming experience and increase your PC’s storage. If you wonder whether you should choose NVMe or M.2, you can continue to read the next part about NVMe vs M.2.
What Is NVMe
Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) is a storage protocol that provides high-speed, efficient communication between a computer’s CPU and SSD. Introduced in 2013, drives using NVMe connect directly to PCIe slots on motherboards, rather than using the traditional SATA interface commonly used by HDDs and older SSDs.
It is an excellent replacement for SCSI (Small Computer System Interface brackets) and ATA (Advanced Technology attachments). These are known as standards for connecting and transferring data between the target storage device and the host system.
Unlike SATA, which was originally designed for slower HDDs, NVMe takes full advantage of the low latency and high-speed capabilities of SSDs.
NVMe is designed for faster media. The main benefits of using NVMe PCIe SSDs are higher output or input operations per second and reduced latency compared to any other type of storage. The SSD storage type has recently gained popularity and is one of the most popular media for storage needs.
What Is M.2
An M.2 drive, also known as a Next Generation Form Factor (NGFF) drive, is a type of SSD that connects directly to a computer’s motherboard using an M.2 interface, eliminating the need for cables. There are three different types of M.2 SSD cards – SATA, AHCI, and NVMe.
M.2 SSDs are smaller and faster than traditional 2.5-inch SSDs, making them popular in gaming setups because they take up less space. They are also more energy efficient than other types of SSDs, extending the battery life of portable devices.
M.2 drives are easy to install and can be added to most modern motherboards with M.2 slots. Users looking to improve their gaming setup with an M.2 SSD will need to make sure their motherboard has an M.2 slot.
If your motherboard does not have an M.2 slot, you can use an M.2 drive by using an adapter card that fits into a Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) slot. So, before you buy an M.2 SSD, you need to know which interface your computer will accept – M.2 SATA or M.2 PCIe.
NVMe vs M.2
There are several factors to consider when choosing the best drive for you. The following is a quick chart about NVMe vs M.2.
| M.2 | NVMe | |
| Form Factor | The form factor for storage devices, including SATA and NVMe SSDs. | Stands for Non-Volatile Memory Express, a protocol for accessing solid-state storage devices. |
| Physical Size | Drives can vary but are typically smaller than 2.5-inch SATA SSDs. | Drives come in the M.2 form factor but can also be found in other factors such as add-in cards and U.2. |
| Performance | Depends on the interface used: NVMe M.2 drives offer significantly faster read/write speeds than SATA M.2 drives. | Offers faster read/write speeds and lower latency compared to SATA and SAS SSDs due to the NVMe protocol. |
| Cost | M.2 SATA drives can be less expensive than NVMe M.2 drives, but the cost also varies based on storage capacity and other factors. | NVMe drives can be more expensive than SATA drives, but the cost varies based on storage capacity and other factors. |
Next, we will provide more details for NVMe vs M.2 in different aspects.
NVMe vs M.2: Form Factor
When talking about SSD form factors, one can refer to the M.2 form factor, its compact size, and various other form factors available for NVMe drives. Understanding the relationship between form factor and performance is critical because using the NVMe protocol can significantly improve SSD performance regardless of form factor.
NVMe is a protocol for accessing data on SSDs that has no direct impact on the drive’s form factor. NVMe drives are available in a variety of form factors including M.2, U.2, add-in card (AIC), and more. The choice of intended use case and physical constraints determine the form factor of a device using SSDs.
NVMe vs M.2: Performance
Both M.2 and NVMe affect computer performance but in different ways. Compared with traditional SATA SSDs, M.2 SSDs can improve performance because it does not require cables, which reduces latency and enables faster data transfer speeds.
NVMe drives increase the data transfer speed of your computer. This faster data transfer speed significantly enhances your computer’s overall performance, especially when working with large files or applications that require reading and writing large amounts of data.
NVMe also supports a deeper command queue than AHCI, allowing more commands to be executed in parallel, further improving performance. NVMe has lower latency than AHCI, resulting in faster response times when accessing data. These improvements reduce boot time, speed up application startup, and improve overall system performance.
NVMe vs M.2: Speed
NVMe and M.2 drives are not directly comparable in terms of speed because they involve different aspects of storage technology. NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a storage protocol that provides high-speed communication between a computer’s CPU and SSD. It is designed to take full advantage of the capabilities of SSDs and can provide faster data transfer speeds than traditional interfaces such as SATA.
M.2, on the other hand, refers to the physical form factor or connector used for storage devices, including SSDs. M.2 drives can support a variety of interfaces, including NVMe, SATA, and more. The speed of an M.2 drive depends on the specific interface it uses. NVMe M.2 drives utilizing the NVMe protocol can provide faster speeds than M.2 drives using the SATA interface.
In conclusion, NVMe is a storage protocol that can be implemented in various form factors, including M.2, and NVMe drives tend to offer faster speeds than M.2 drives using the SATA interface.
NVMe vs M.2: Computer Compatibility
NVMe compatibility with computers depends on software and hardware support. NVMe requires a computer with UEFI firmware, NVMe drivers, and an M.2 slot. Some older computers may not support NVMe or require a firmware update to enable support.
For M.2 drives, we take physical attributes into account when evaluating compatibility. The presence and size of the M.2 slot are critical in determining which M.2 drive to use in a particular computer. M.2 slots are increasingly common in newer computers, but may not be present in older models.
NVMe vs M.2: Which One to Choose
M.2 provides a compact form factor for SSDs, while NVMe provides faster data transfer speeds and lower latency than SATA. Depending on the specific requirements and use cases of the device, M.2 and NVMe can be combined for optimal performance.
Selecting the right combination of technologies to meet your specific needs and ensure optimal system performance is critical. If you need a high-performance storage solution, NVMe is the better choice. If you need a compact and versatile form factor, M.2 is the better choice.
In some cases, you can even use NVMe and M.2 together, taking advantage of the protocol and form factor for maximum performance.
Migrate the System to NVMe or M.2 SSD
Whether you choose NVMe or M.2 SSD, you may want to migrate your system to it to get better performance, then you can use the free backup software – MiniTool ShadowMaker to do that.
It is a professional backup program that can be used to back up the operating system, disk, partition, file, and folder. Clone Disk is another useful feature of MiniTool ShadowMaker, which is significant for hard drive upgrading.
Is it better to make a clone? This depends on the actual situation. If you need to upgrade the disk to a larger one without reinstalling OS, cloning is recommended. If you want to back up disk data to an image file, cloning cannot realize it but the backup feature can.
How to Migrate OS with MiniTool ShadowMaker
Now, let’s see how to migrate your operating system to NVMe or M.2 SSD with MiniTool ShadowMaker’s Clone Disk feature.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
Step 1: Connect the NVMe or M.2 SSD to your computer. Launch MiniTool ShadowMaker, and click Keep Trial to continue to use the Trial edition.
Step 2: After entering the main interface, go to the Tools tab and choose the Clone Disk feature to continue.
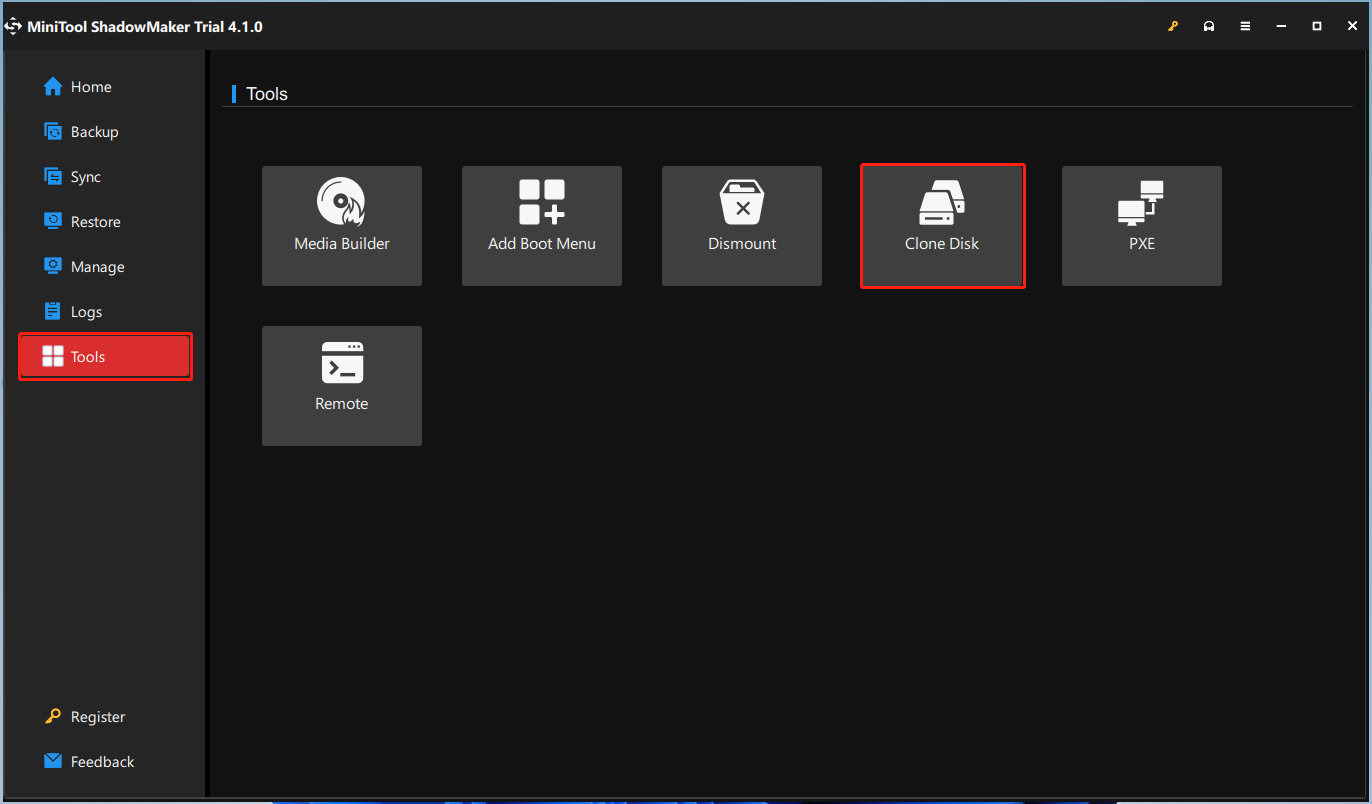
Step 3: Next, you are required to choose the source disk and the target disk for cloning.
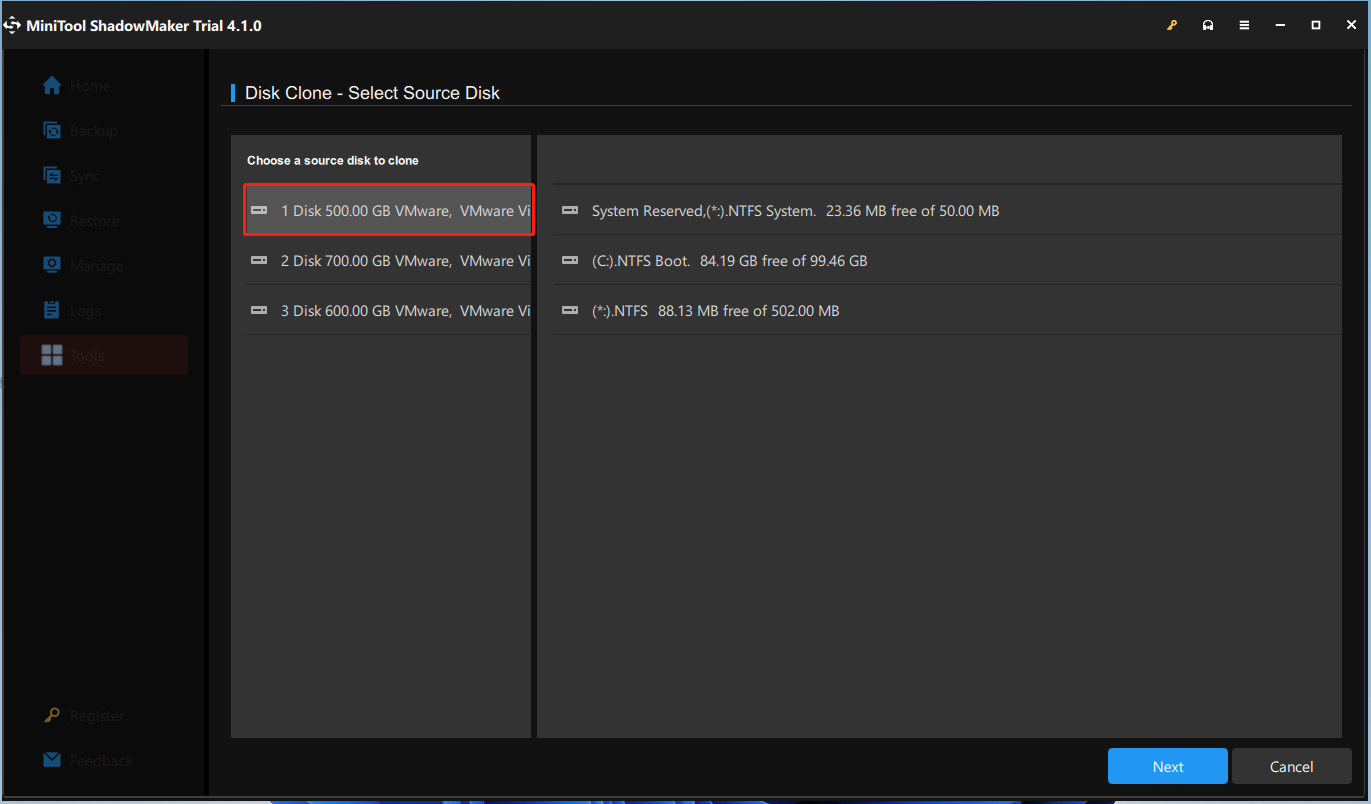
Step 4: After you have successfully selected the disk clone source and destination, click Start to continue.
Step 5: Then you will receive a warning message that tells you all data on the target disk will be destroyed during the disk cloning process. Then click OK to continue.
Step 6: Then it will begin to clone the system to SSD and you need to wait several minutes until the process is finished.
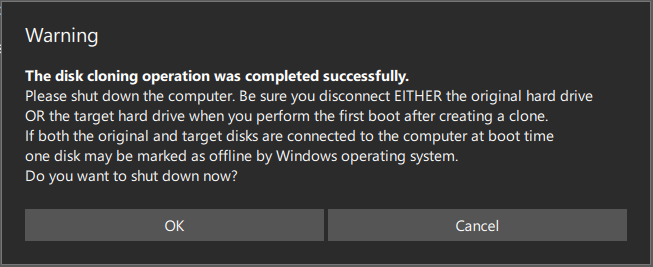
Step 7: When the disk clone process is finished, you will receive a message which tells you that the source disk and the target disk have the same signature. Thus, you need to remove the old HDD or SSD from your computer and insert the new one into the PC.
Related posts:
- How to Clone SSD to Larger SSD on Windows 11? Here Are 2 Tools!
- How to Clone Hard Drive via Command Prompt? Here Are 2 Ways!
Bottom Line
In this post, you have got some information about flash NVMe vs M.2. Then, you know the answer to this question – which one should you choose? Besides, if you want to clone the system to SSD without reinstalling OS, MiniTool ShadowMaker is a helpful tool.
If you have any other ideas about the differences between NVMe and M.2 or any questions related to MiniTool software, contact via [email protected] and we will reply to you as soon as possible.

