Both NAS and cloud are a kind of remote storage. They share some functions in common but, at the same time, they can be distinguished in many ways. This article about NAS vs cloud will show you their differences and tell you which one is better. For more details, you can read this post on MiniTool Website.
What Is Cloud Storage?
With the universal application of cloud sync and cloud backup, the cloud has become a word that is commonly used in the technology field. Cloud storage tools emerge in endlessly, such as Dropbox, Google Drive, pCloud, and OneDrive.
Cloud storage is a cloud computing model that stores data on the Internet through a cloud computing provider that manages and operates data storage as a service.
It delivers on-demand with immediate capacity and cost, eliminating the need to buy and manage your own data storage infrastructure. It allows you to transfer data on an offsite storage system and access them whenever needed.
There are four types of cloud storage:
- Private cloud storage – a storage mechanism for storing organizational data on internal storage servers by implementing cloud computing and storage technologies. It provides the usability, scalability, and flexibility of the storage architecture.
- Public cloud storage – a service model that provides data storage on a pay-per-use basis.
- Hybrid cloud storage – a type of data center infrastructure that combines private and public clouds, along with on-premises resources, and can share data across all environments.
- Community cloud storage – a shared cloud computing service environment that is targeted to a limited set of organizations or employees.
What Is NAS?
NAS (Network Attached Storage) is a device that is connected to the Network and has the function of storing data. It is a dedicated data storage server.
Data-centric, it separates storage devices from servers and centrally manages data to release bandwidth, improve performance, reduce total cost of ownership, and protect the investment. The cost is much lower than using server storage and the efficiency is much higher.
NAS vs Cloud
You may have mastered their definitions to some extent. For a better understanding of NAS vs cloud storage, you can see their distinctions from several aspects.
Cost
To weigh the value of NAS and cloud, you can think of their devices. Cloud can perform well without the device demands compared to NAS but the service subscription fees are required.
In other words, if you only need a limited amount of storage that is within the free storage from the provider, it can be regarded as a cost-effective deal, otherwise, you can think about buying a NAS device for your large amounts of storage demands.
It is hard to compare their price. You need a comprehensive consideration of how much storage you need. For long-term use, NAS may be a good choice.
Security
For NAS users, you can take the necessary and robust measures to protect your data. For example, you can make sure you’re following basic security principles like using secure passwords, updating software and firmware regularly, and avoiding opening suspicious email attachments.
For cloud users, the security level depends on the cloud service provider. You can choose a more reliable service but it is less independent compared to NAS.
As time goes by, cloud service providers also attach more importance to data security. The files stored on cloud servers are encrypted and servers are usually located in warehouses that most workers don’t have access to. You can trust those dedicated companies.
Ease of Use
NAS devices are becoming more user-friendly and these consumer-facing products require minimal setup and configuration, but they still can’t compete with the ease of use of cloud services.
Most major cloud services are desktop apps that make you use remote storage seamlessly.
Performance
In the comparison of their performance, NAS is superior to the cloud. The speed of cloud transfer or backup is closely related to your network speed and the data you are prepared to use.
But one good thing is that cloud service apps will not use the maximum bandwidth so that they don’t choke your Internet connection entirely.
While the NAS speeds here will be considerably faster than uploading over the Internet for it is attached to your computer directly over Wi-Fi or a wired connection.
Setup and Maintenance
For NAS users, they need to set up the hardware and connect the device to the network. And the device is always accessible for upgrades or repairs.
While for cloud users, cloud providers here hold all the cards because there is barely any setup. You may only need to install an app. And you don’t need to worry about the maintenance issue, because cloud services will take care of that without their users ever noticing.
Backup and Reliability
As for NAS vs cloud backup, it’s the major difference between them.
NAS – local backups on your NAS device.
If your NAS devices can accommodate more than one hard drive, you can enjoy higher reliability. They will work with backup software and protect you against the failure of one of the drives.
But there is a deadly defect – if your NAS device breaks down, gets stolen, or is destroyed in a fire, your files might be gone forever.
Cloud – automatic backups on a remote server.
Your backup data will be kept by the cloud companies. Your data will be safe as long as the service won’t go down or be under some severe attacks.
Storage Limitation
NAS device storage size depends on the number of drives you have. The more drive you have installed in your NAS, the more storage you will get.
The storage capacity of the cloud is lower compared to NAS. But for its free maintenance, you don’t need to worry about its upgrade. You just need to pay for the service provider and you can get easily upgraded.
Pros and Cons
Cloud:
Pros:
- Flexibility and ease of access – stakeholders can access assets stored on the cloud from a location and device of their choice without the hassle of downloading or installing them.
- Remote management support – cloud storage paves the way for remote management.
- Fast scalability – one of the main benefits of cloud storage is that you can provide new resources with just a few mouse clicks, without requiring any additional infrastructure.
- Redundancy for backup – in the event of a natural disaster, accident, or cyber attack, the cloud ensures that your data is safely stored in a remote location. Data redundancy means replicating the same data in multiple locations and that is essential for a backup mechanism.
- Cost savings – cloud storage can greatly reduce your costs in hardware devices, storage facilities, and power supplies.
Cons:
- Outage and downtime risk – cloud platforms managed by external providers can have outages that make data and applications stored in these environments inaccessible. In this way, you need additional redundancy for your most critical data.
- Security issue – public cloud environments are shared by multiple tenants, which can increase your security vulnerabilities.
- Supplier lock-in risk – if all your data is stored in a single public cloud platform, there’s a risk of vendor lock-in and potential inflexibilities.
NAS:
Pros:
- NAS is a better choice for users who need to transfer file data to multiple clients over a network. – NAS devices work well in environments where data must be transmitted over long distances.
- Easy deployment – NAS hosts, clients, and other devices can be widely distributed across an enterprise network environment. NAS can provide reliable file-level data consolidation because file locking is handled by the device itself.
- It can be used in efficient file sharing tasks – different hosts and clients access NAS data using file sharing protocols to implement file sharing.
Cons:
- Data backup or storage occupies network bandwidth – the NAS device is connected to the client over an enterprise network. This will inevitably affect other network applications on the enterprise’s internal network.
- Sharing network bandwidth is a major problem that limits NAS performance. Therefore, the data transfer rate of the NAS system is not high.
- NAS scalability is limited by device size – it is very easy to add another NAS device, but it is not easy to seamlessly merge the storage space of two NAS devices, because NAS devices usually have unique network identifiers and storage space expansion is limited.
- It can only provide file storage space, but cannot fully meet the requirements of database applications.
- Upfront installation and equipment costs are high.
MiniTool ShadowMaker
The above part has told you the difference between NAS and cloud. They boast of their advantages and show their functions on their own stage. You can choose between them based on their pros and cons.
In some ways, NAS can give you additional storage space, easier collaboration, and less mess. Your data security can be reassured. Besides, it can be your own private cloud and be used as your media server.
If you want to do a NAS backup, here, it is recommended to try this wonderful backup tool – MiniTool ShadowMaker.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
You can download and install the program first and you will get a free trial version for 30 days.
Step 1: Open the MiniTool ShadowMaker and click Keep Trial on the top right corner.
Step 2: Click the Source section and in the pop-up window you can choose backup content. Here, MiniTool ShadowMaker provides you with more options, including the system, disk, partition, folder, and file. By default, the system has been set as the backup source already.
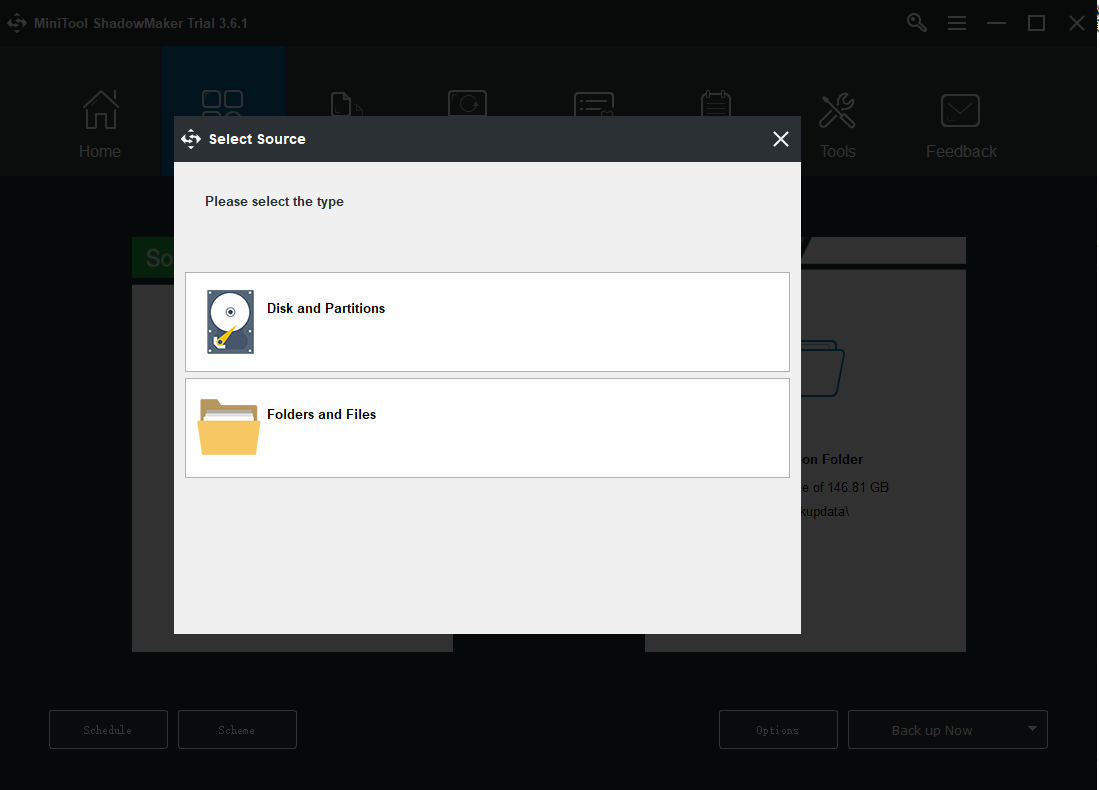
Step 3: Go to the Destination part where you can see four options containing the Administrator account folder, Libraries, Computer, and Shared.
If you want to back up to NAS, please choose Shared and click Add new button, and type the path, user name, and password. And then click OK to save your changes.
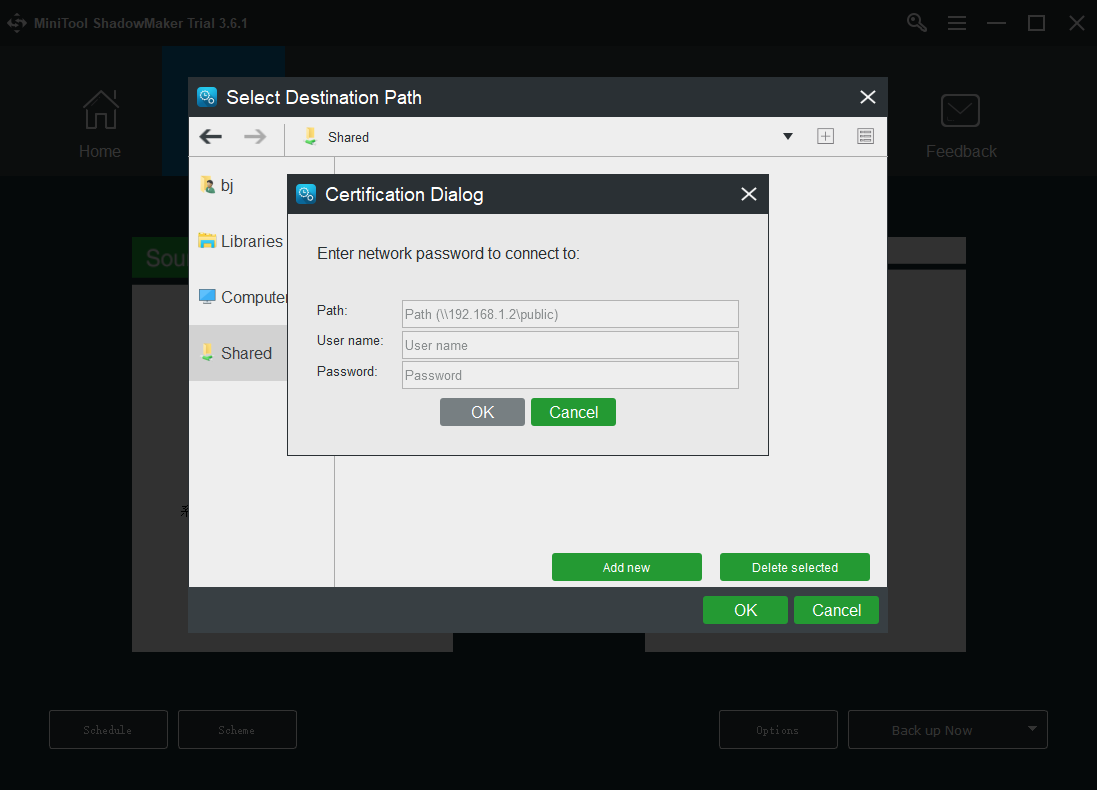
Step 4: Click the Back up Now option to start the process immediately or the Back up Later option to delay the backup. The delayed backup task is on the Manage page.
Bottom Line:
Cloud storage is commonly used in daily life and its name has become a household word. By learning this article about NAS vs cloud, you may have your understanding of NAS. You can weigh the pros and cons and make your choice between them.
If you have encountered any issues when using MiniTool ShadowMaker, you can leave a message in the following comment zone and we will reply as soon as possible. If you need any help when using MiniTool software, you may contact us via [email protected].
NAS vs Cloud FAQ
Modern NAS has a cloud option that allows the user to access the data saved on it via the Internet and we can consider it as a private/personal cloud. However, its performance and storage capacity of it could not compete with the cloud services that are using powerful servers and data centers.
What we use to store our data like NAS on the cloud are mostly SAAS services such as Google Drive, Dropbox, Box, Amazon S3, Microsoft One Drive, and more.
For a true cloud-like experience it should be, but if you want to maximize your security options, you can restrict just to your network. Even though NAS devices are becoming more user-friendly, with the products requiring minimal configuration, they still cannot compare to the ease of a cloud service.
Both NAS and cloud-based backup can offer solid data protection. If a faster backup is desired, with a primary goal of protecting incremental changes, then a NAS-based approach might be better.