This article created on MiniTool official website compares two Windows data protection utilities, OneDrive and File History. It covers 5 aspects of their differences and helps you know them better.
Update 08/12/2021: Microsoft has replaced File History in Windows Settings with OneDrive in current Windows 11 preview build 10.0.22000.120. Learn more >> What are the differences between File History and OneDrive? Just read the below content.
What Is File History?
File History is a Windows 10 built-in tool to automatically back up your computer files or folders to another hard drive so as to protect those files/folders from losing.
What Is OneDrive?
On the one hand, OneDrive is a cloud storage service managed by Microsoft for users to save and transfer data. Together with Google Drive and Dropbox, they are the three most popular cloud drives.
On the other hand, OneDrive also plays as a file sync/backup service to sync files/folders between the OneDrive cloud and the local machine.
#1 File History vs OneDrive: Backup Content
According to the definition and function of OneDrive and File History, it seems that they are similar in backup content. Yet, there are still some differences.
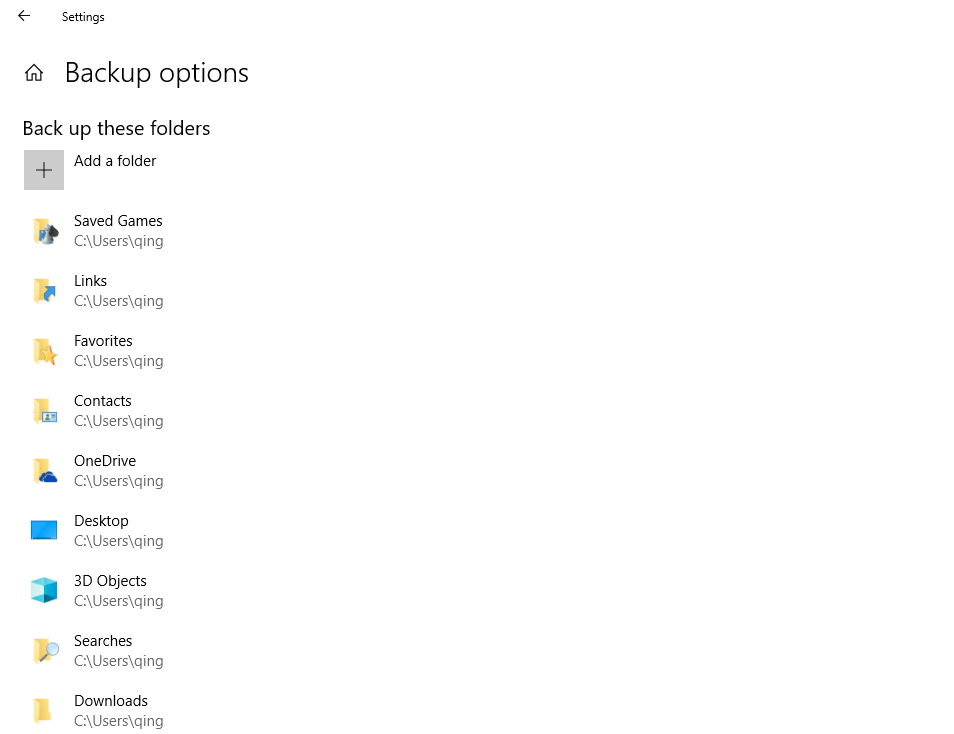
Backup Content of File History
The default folders that will be backed up by File History are listed below and most of them locate in C:\Users\<username>. Of course, you can add extra folders and files or exclude some folders from the default list.
- Saved Games
- Links
- Favorites
- Contacts
- OneDrive
- Desktop
- 3D Objects
- Searches
- Downloads
- Pictures
- Documents
- Videos
- Music
Backup Contents of OneDrive
Since OneDrive is a two-way sync program, you can make use of it to sync any items in your OneDrive cloud to your local PC. The source is also the sync copy and the sync copy is also the source.
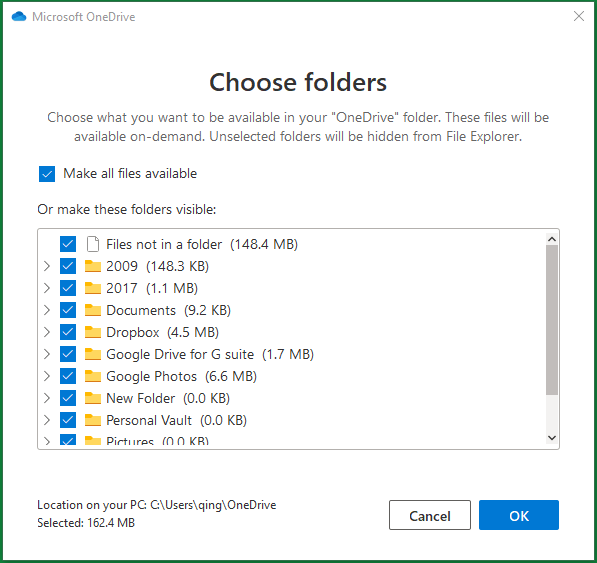
Also, you are able to synchronize selected folders to OneDrive cloud, Desktop, Document, or Pictures.
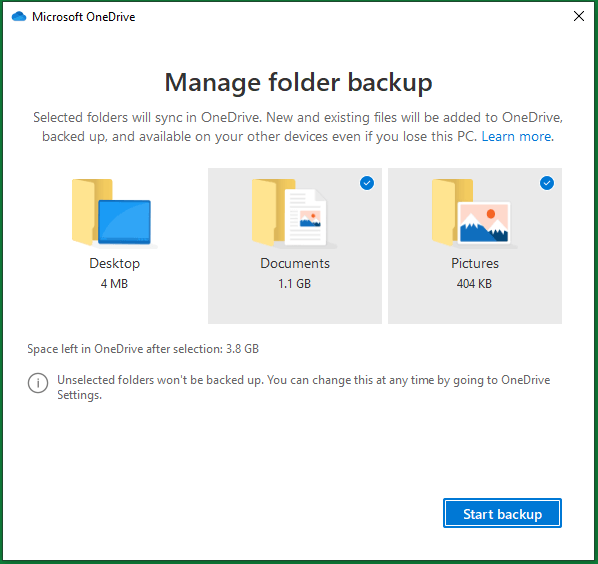
As for protecting local files/folders, it seems that File History covers much more content than OneDrive.
#2 Microsoft File History vs OneDrive: Backup Frequency
The backup frequency refers to how often the backup task takes place. OneDrive provides real-time continuous data protection while the highest File History backup frequency can only be every 10 minutes.
That is to say, OneDrive synchronization carries out immediately when there is a change happens to a target file or folder. For example, when a new file is created within one of the target folders, an old file is deleted, or something edited within some target files.
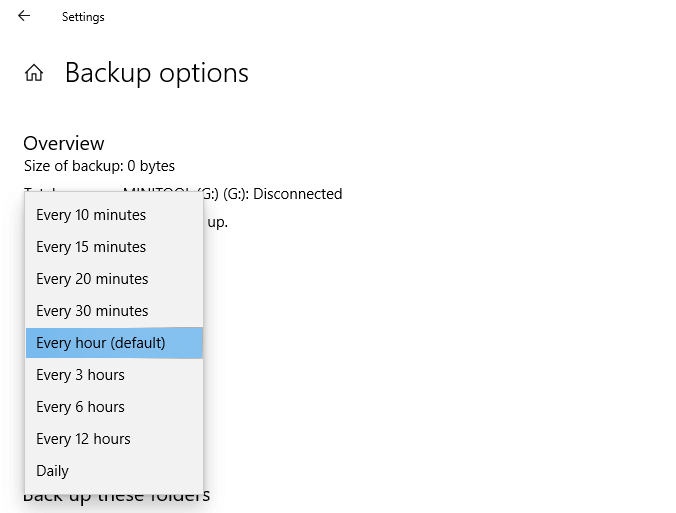
Whereas the period between two File History backups is at least 10 minutes, no matter there is a change or not. You can also alter the time interval to every 15 minutes, every 20 minutes, every 30 minutes, every hour (default), every 3 hours, every 6 hours, every 12 hours, or every day.
#3 Windows 10 File History vs OneDrive: Backup Destination
As for where to save the backup image files, it is quite different between File History and OneDrive. For File History, you can backup to another hard disk drive no matter it’s internal or external, just not the same drive as the source one is OK. Also, the backup destination can be a network location. It should be large enough to save the current backup image and several future backup images, the larger the better to some extent.
For OneDrive, the backup target location is set. If you sync from a local computer, you can only save the copy in your OneDrive cloud. If you sync from the online cloud, the sync copy will be stored in the OneDrive folder locating in C:\User\<username>.
#4 OneDrive vs File History: Backup Version
Actually, for OneDrive, there is no backup version since it’s a real-time syncing service. It reflects the changes immediately from the source side to the destination side. Thus, there is only one copy of the source files in the destination and it’s always up-to-date.
For File History, things are different and there do have different copies of the source files. Each time a backup is made, a backup image is created, no matter what the backup frequency is.
The backup version of both OneDrive and File History will become larger and larger. Yet, both of the two data protection services enable you to manage backup versions to save destination space. For OneDrive, you can turn on the Files On-Demand feature to only download files from the cloud to local when you use them. Otherwise, you will only see the files list on your computer.
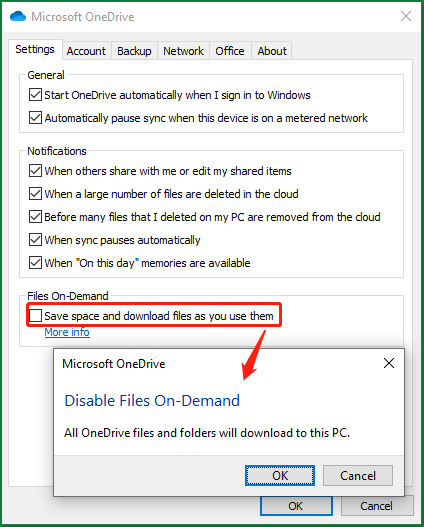
For syncing from local to cloud, just put import files into the local OneDrive folder and they will be automatically synced to the cloud. So, you don’t have to select any other local folder to sync.
Moreover, clear out the files you don’t want to sync anymore can also save you some storage space. Yet, you are recommended to copy those files outside of the OneDrive folder to another place of your local machine for deleting them from either the local OneDrive folder or online cloud will also remove them from the other side.
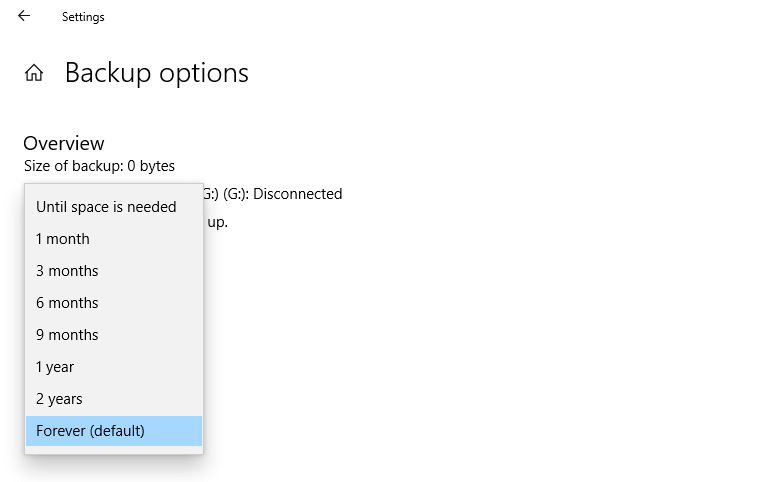
For File History, you can specify how long you’d like to keep your backup images, until space is needed, 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 9 months, 1 year, 2 years, or forever (default).
#5 File History vs OneDrive: File Recovery
This can be the most important part of both data security services. If you can’t restore lost or damaged files from their backups, the backups worth nothing!
For File History, since there are many backup versions, you can choose the right backup point to restore. Usually, the very last image version will be selected since it’s the closest version to the lost files. And, you can select to only restore some of the files/folders.
As for OneDrive, there is no file restoration since it’s a real-time synchronization. However, if you accidentally delete a file from either the local OneDrive folder or the OneDrive cloud, it will also be removed from the other side. The lucky part is that if you haven’t permanently deleted the file within 30 days, you can retrieve it from either the online OneDrive recycle bin or your local computer recycle bin.
OneDrive and File History Alternative – MiniTool ShadowMaker
According to the above content, both File History and OneDrive have advantages and disadvantages. There is a third-party program named MiniTool ShadowMaker that inherits the pros and avoids some cons of OneDrive and File History.
MiniTool ShadowMaker TrialClick to Download100%Clean & Safe
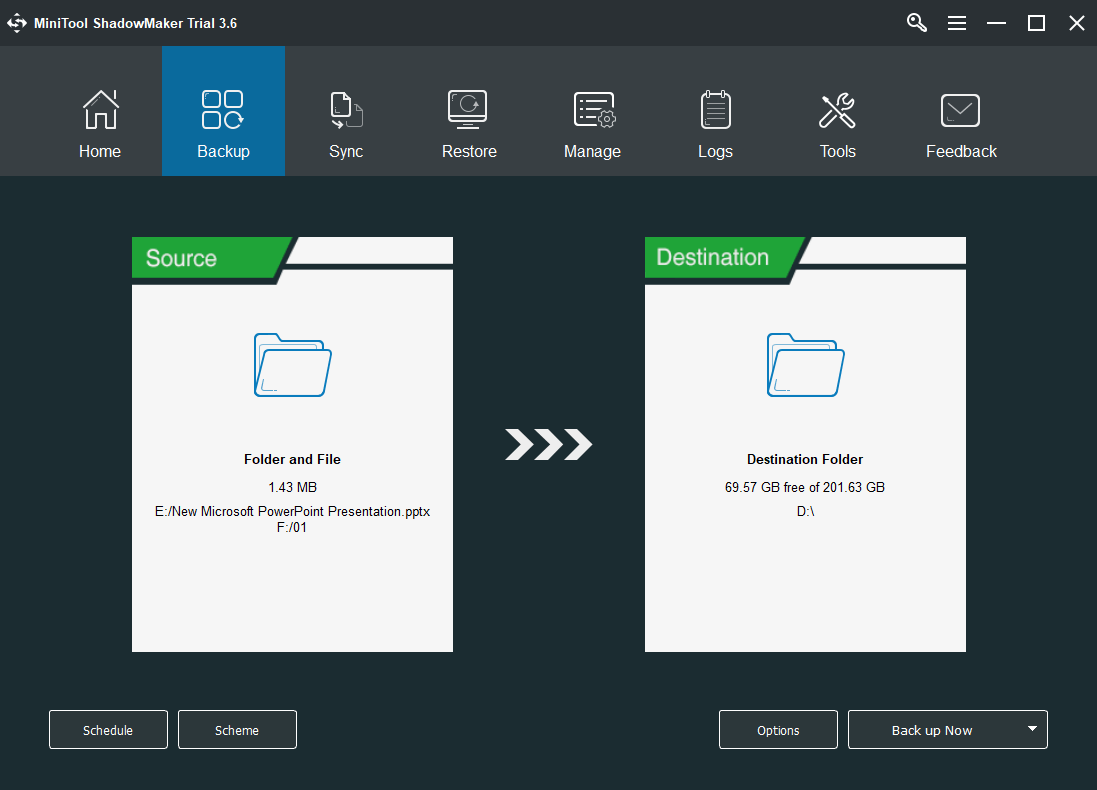
MiniTool ShadowMaker can back up not only files/folders but also partitions/volumes, operating systems, and even the whole hard disks (internal or external). It adds more backup frequencies generally including daily, weekly, monthly, and on a special event.
MiniTool ShadowMaker allows you to back up source to internal or external hard drives, removable disks (USB flash drive, SD card, thumb drive, etc.), as well as network locations (NAS or shared storage space).
MiniTool ShadowMaker stores backup images relying on the backup method you choose, full, incremental, or differential backup, and helps you save your storage space. Accordingly, you can select any restore point to recover the files once the original ones are lost or damaged. Moreover, you can choose to restore to the original location or different place and even another computer.

![[Full Review] Windows 10/11 Backup Options of File History](https://images.minitool.com/minitool.com/images/uploads/2021/05/windows-10-backup-options-thumbnail.png)