What is 3D NAND? Why should you choose 3D NAND SSD? What are the differences between 3D NAND and traditional NAND hard drive? This post from MiniTool shows you the differences between 3D NAND and V NAND. In addition, you can visit MiniTool to find more Windows tips and solutions.
What Is 3D NAND?
3D NAND, also called V NAND, is the stacking of memory chips on top of each other. The 3D NAND is a type of non-volatile flash memory in which the memory cells are stacked vertically in multiple layers. The purpose of 3D NAND technology is to make your device faster, hold more information, run more efficiently and use less energy.
The 3D NAND concept has been put forward with for several years but it has been put into practice recently. Samsung is first manufacturer adopting the 3D NAND technology. The Samsung SSD 850 Pro used the 3D NAND technology.
How Does 3D NAND Work?
Flash memory is an advanced type of electrically erasable programmable read-only memory. This kind of non-volatile memory holds firmware such as the BIOS in a PC. Flash memory stores data in arrays of transistors, which can be designed to store one, two, three or four data bits.
With older and more traditional EEPROMs, a flash memory cell must be erased before can be rewritten. An EEPROM erases data byte by byte. However, in a flash memory device, tunnel electrons clear any charge on the floating gate in a flash. As a result, the name flash memory enables contents to be rewritten.
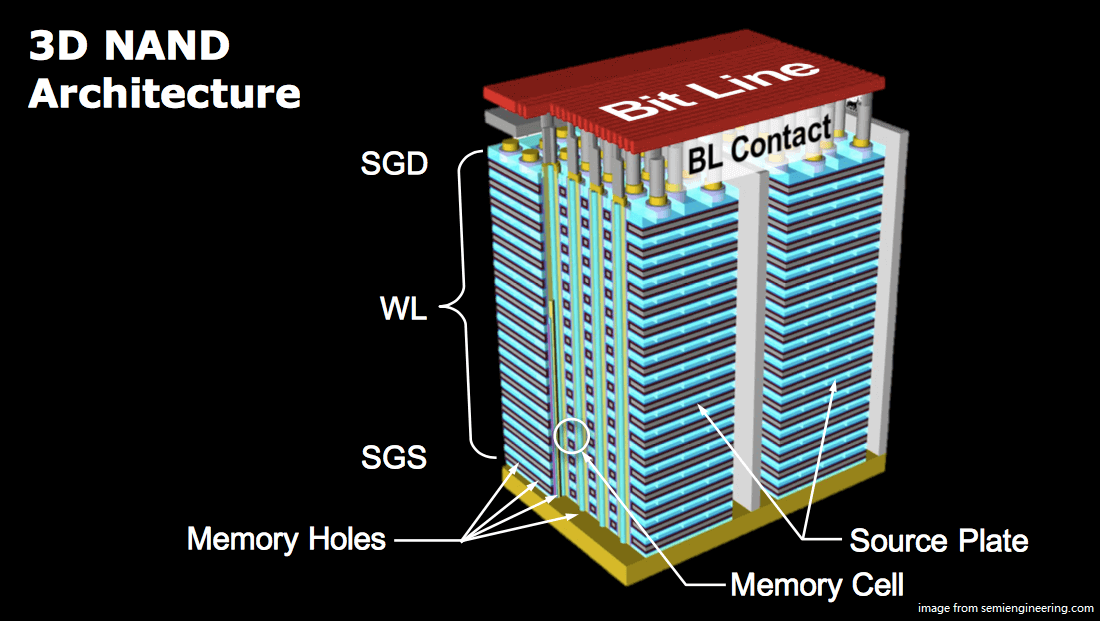
In order to move 2D NAND to 3D NAND, the fabrication process adds multiple layers of memory cells on top of each other, along with interconnections between the layers. A typical 3D NAND flash chip can easily include 32 to 48 individual layers, with 64-, 96- and even 128-layer devices coming. In addition, the increase of layer makes it more difficult to manufacturer. However, the layer implements greater bit density within the storage device with much shorter connection paths, which leads to better performance.
So, after learning some basic information about 3D NAND, do you know what the differences between 3D NAND and traditional 2D NAND flash are? So, in the next part, we will show some of them.
What Are the Differences Between 3D NAND and 2D NAND?
Both 3D and 2D NAND flash memory devices are available today. Then do you know what their differences are?
Capacity: 3D NAND flash memory devices offer greater storage capacity or data density, compared to 2D NAND flash. Stacking multiple layers of memory cells to create a three-dimensional storage matrix is able to bring large hard drive capacity.
Performance and Power: When memory cells are laid out in a 2D matrix, there is a finite distance to move bits to and from cells. The distance equates to time or latency. In a 2D NAND device, the distance will increase and decrease the performance of larger 2D NAND flash devices. So, the 3D NAND devices enjoy better performance. In addition, 3D NAND flash memory can be written in a single pass and uses up to 50% power than 2D NAND.
Cost: There is a close relationship between cost and per byte. Compared with 2D NAND flash memory, 3D NAND flash memory is able to vastly lower the cost-per-byte. In other words, the 3D NAND devices will be more cost-effective than 2D NAND devices.
Final Words
To sum up, this post has shown what the 3D NAND is, and also shown some differences between 3D NAND and 2D NAND. If you have any different ideas of 3D NAND, share it in the comment zone.